Are you ready to transform your organic waste into a treasure trove of nutrient-rich soil? Composting is the key to unlocking the power of nature's recycling process. This comprehensive guide will take you by the hand and empower you with all the knowledge and step-by-step instructions you need to become a composting master.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 219 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 58 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Benefits of Composting
- Enriches soil fertility: Compost adds organic matter, nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms to soil, promoting plant growth and overall soil health.
- Reduces waste: By composting organic materials, you can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Saves money and resources: Composting eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers and reduces the consumption of water and energy.
- Protects the environment: Landfill waste decomposes anaerobically, releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Composting, on the other hand, releases oxygen and carbon dioxide, which are less harmful to the environment.
Types of Composting
There are two main types of composting: aerobic and anaerobic.
- Aerobic composting: This is the most common type of composting. It requires oxygen to break down organic materials. Aerobic composting is typically done in a compost pile or bin.
- Anaerobic composting: This type of composting does not require oxygen. It is typically done in a closed container, such as a compost digester or septic tank.
How to Compost
Materials you need:
- Organic materials (see below)
- Compost bin or pile
- Water
- Compost starter (optional)
Organic materials for composting:
- Kitchen scraps (fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds)
- Yard waste (leaves, grass clippings)
- Manure (from herbivores)
- Paper products (newspaper, cardboard)
- Wood chips or sawdust
Step-by-step instructions:
1. Choose a compost bin or pile
There are many different types of compost bins and piles available. Choose one that is the right size for your needs and is made of durable materials.
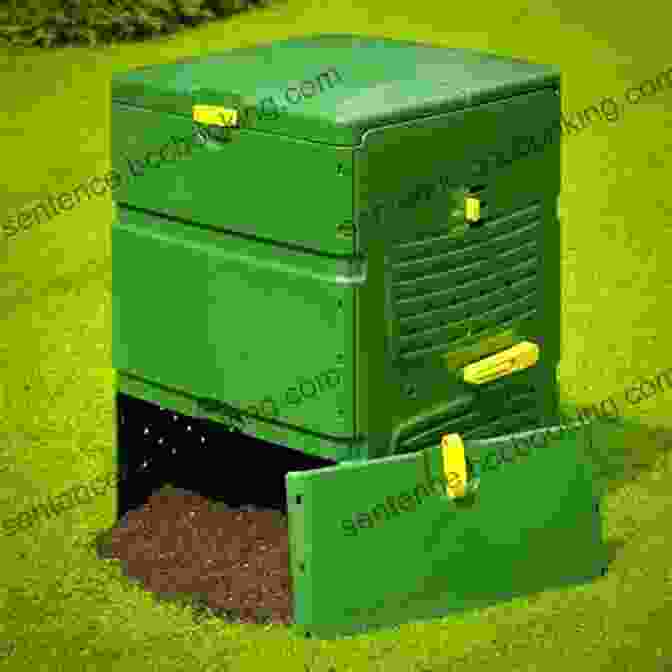

2. Add organic materials
Start your compost pile by adding a mixture of organic materials. Include a balance of "brown" materials (such as leaves, paper, and sawdust) and "green" materials (such as kitchen scraps, grass clippings, and manure).
3. Water and mix
Water your compost pile regularly to keep it moist, but not soggy. Use a shovel or pitchfork to turn and mix the compost every few days. This will help to aerate the pile and speed up the decomposition process.
4. Add compost starter (optional)
Adding a compost starter to your pile can help to jumpstart the decomposition process. Compost starters contain beneficial bacteria and fungi that will break down organic materials more quickly.
5. Wait and observe
Composting takes time. It can take several months for organic materials to fully decompose. Be patient and observe your compost pile regularly. You will know it is ready to use when it has turned dark and crumbly.
Troubleshooting Composting Problems
If you are having problems with your compost pile, there are a few things you can check.
- Compost pile is not heating up: This could be due to a lack of moisture or oxygen. Add water or turn the pile more frequently.
- Compost pile is smelly: This could be due to too much nitrogen-rich materials. Add more brown materials, such as leaves or cardboard.
- Compost pile is attracting pests: This could be due to a lack of oxygen or too much moisture. Turn the pile more frequently and add more brown materials.
Using Compost
Once your compost is ready to use, you can apply it to your garden or lawn to improve soil fertility. Compost can also be used as a potting mix for indoor plants.
- Add compost to garden beds: Mix compost into the top 6-8 inches of soil before planting.
- Use compost as a mulch: Spread a layer of compost around your plants to help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and add nutrients.
- Use compost in potting mixes: Add compost to potting mixes to improve drainage and fertility.
Composting is a rewarding and eco-friendly way to recycle organic waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your garden. With the knowledge and instructions provided in this guide, you can become a composting master and unlock the transformative power of nature's recycling process.